 您的购物车当前为空
您的购物车当前为空
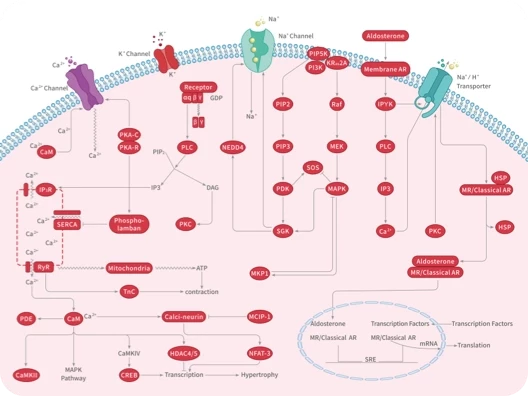
钙离子探针
钙离子探针是一类用于检测细胞内钙离子浓度变化的荧光染料,通过与钙离子结合引起荧光强度或波长的变化实现定量分析。广泛应用于细胞信号传导、肌肉收缩机制及神经活动研究。
- BAPTA-AMBAPTA/AMT6245126150-97-8BAPTA-AM 是一种钙离子螯合剂,具有细胞渗透性和选择性,可以阻断 hERG、hKv1.3 和 hKv1.5 通道 (IC50=1.3/1.45/1.23 μM)。BAPTA-AM对 Ca2+的亲和力是 Mg2+的 105 倍,可以用于钙在细胞信号传导中的作用。
- ¥ 197
规格数量 客户已引用
客户已引用 - Fura-2 AMFura-2 Acetoxymethyl esterT18995108964-32-5Fura-2 AM是一种膜渗透的Ca2+(钙离子)指示剂,在细胞内被酯酶esterase转变为Fura-2。Fura-2 AM的荧光发射波长在510 nm左右,在高钙浓度和低钙浓度下分别显示出340和380nm的激发最大值,可以用荧光强度比计算钙离子浓度。
- ¥ 3290
规格数量 - OG 488, SEOregon green 488 succinimidyl ester, OG488,SE, OG488, SET39402198139-51-4OG 488, SE(Oregon green 488 succinimidyl ester)是一种绿色荧光染料,在生理pH范围内(pH=6-8)对pH不敏感,可用于监测活细胞或微生物的增殖。
- ¥ 768
规格数量 - Alizarin Complexone茜素络合指示剂, Alizarin-3-methyliminodiacetic acid, Alizarin Fluorine BlueT199633952-78-1Alizarin Complexone (Alizarin-3-methyliminodiacetic acid) 是 Rous 相关病毒 2 逆转录酶的抑制剂。 Alizarin Complexone 可用作生物研究的钙示踪剂和螯合剂。
- ¥ 175
规格数量 - BAPTA tetrapotassiumBAPTA, tetrapotassium salt, BAPTA 四钾盐TD009773630-08-7BAPTA tetrapotassium是一种选择性的钙离子螯合剂,还能够抑制phospholipase C的活性,可用于研究细胞内钙稳态、控制细胞毒性和控制金属离子干扰。
- ¥ 189
规格数量 - Fura-2 potassium saltT37759113694-64-7Fura-2 potassium salt 是一种常用的紫外光激发性荧光探针,可用于细胞内钙离子成像。
- ¥ 1430
规格数量 - Fura-FF pentapotassium saltT37761192140-58-2Fura-FF pentapotassium salt 是一种低亲和力的钙荧光染料 (Ex/Em: 365/514 nm, 无钙; 339/507 nm, 高钙)。
- ¥ 1560
规格数量 - Quin-2AMQuin-2 acetoxymethyl esterT1905083104-85-2Quin-2AM is a fluorescent Ca2+ chelator with a high affinity for calcium.
- ¥ 4170
规格数量 - BTC AMT37188176767-94-5BTC AM is a cell-permeable acetoxy-methyl ester of BTC . As BTC AM enters cells, it is hydrolyzed by intracellular esterases to produce BTC. BTC is a low affinity calcium indicator (Kd = 7-26 μM) that displays excitation/emission spectra of 401/529 nm, respectively. It exhibits a shift in the excitation maximum from approximately 480 to 401 nm upon calcium binding, enabling determination of ratiometric calcium measurements. BTC is suitable for detecting elevated calcium levels associated with activation of smooth muscle, neurons, and intracellular calcium stores.
- ¥ 8620
规格数量 - Fura-2 (sodium salt)T37760Fura-2 is a ratiometric fluorescent calcium indicator that can be used to detect calcium in cells. It is a pentacarboxylate that displays excitation maxima of 340 and 380 nm at high and low calcium concentrations, respectively, when the emission is fixed at 510 nm, enabling determination of ratiometric measurements of calcium influx in live cells.
- ¥ 2680
规格数量 - Fluo-3 (ammonium salt)T37315339221-91-9Fluo-3 (ammonium salt) is a fluorescent calcium indicator commonly used in flow cytometry and cell-based experiments to detect changes in intracellular calcium levels. [1] Its absorption maximum at 506 nm makes it compatible with excitation at 488 nm by argon-ion laser sources. Fluo-3 provides intense fluorescence upon binding calcium, detected at a maximum emission at 526 nm which can be monitored by FL1 (green, 525 nm band pass) sensors in flow cytometry.
- ¥ 4930
规格数量 - Calcium Green BAPTA-2 AMT85995163634-11-5Calcium Green BAPTA-2 AM serves as a fluorescent indicator for calcium ions.
- 待询
规格数量 - Fluo-4, pentaammonium saltTD0051Calcium measurement is critical for numerous biological investigations. Fluorescent probes that show spectral responses upon binding calcium have enabled researchers to investigate changes in intracellular free calcium concentrations by using fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry, fluorescence spectroscopy and fluorescence microplate readers. Fluo-3 and Fluo-4 are most commonly used among the visible light-excitable calcium indicators. Fluo-4, pentaammonium salt is an analog of fluo-3 with the two chlorine substituents replaced by fluorines, which results in increased fluorescence excitation at 488 nm and consequently higher fluorescence signal levels.
- ¥ 4200
规格数量 - PAO-NapT363991613402-20-2PAO-Nap is a chemically modified version of PAO, in which a naphthalimide fluorophore is attached to the compound using a linker called aminocaproic acid. This modified compound, PAO-Nap, exhibits a selective targeting of thioredoxin reductase, leading to the induction of apoptosis in HL-60 cells through oxidative stress mechanisms[1].
- ¥ 2397
规格数量 - Rhod-FF AMT37320Rhod-FF AM是一种细胞渗透性的荧光钙离子指示剂,能够被细胞内酯酶水解生成rhod-FF,Ex/Em=552/580 nm。Rhod-FF AM与Ca²⁺的结合亲和力较低,可用于10-200 μM浓度范围的较高浓度钙离子检测。
- ¥ 1560
规格数量 - Fluo-8, AM钙荧光探针Fluo-8, AMTD0055Fluo-8,AM is one of the most commonly used fluorescent probes to detect intracellular calcium concentration.Fluo-8, which penetrates the cell membrane and enters the cell, is cut by the intracellular esterase to form fluO-8, and thus is trapped in the cel
- ¥ 5687
规格数量 - Coelenterazine hcpT36847123437-32-1Coelenterazine hcp is a synthetic bioluminescent luciferin that displays an emission maximum of 445 nm.1It has been used as a calcium indicator and substrate to quantifyRenillaluciferase activity.1,2,3 1.Sabnis, R.W.Handbook of biological dyes and stains: Synthesis and industrial applications(2010) 2.Shimomura, O., Kishi, Y., and Inouye, S.The relative rate of aequorin regeneration from apoaequorin and coelenterazine analoguesBiochemistry Journal296(Pt 3)549-551(1993) 3.Pichler, A., Prior, J.L., and Piwnica-Worms, D.Imaging reversal of multidrug resistance in living mice with bioluminescence: MDR1 P-glycoprotein transports coelenterazineProc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA.101(6)1702-1707(2004)
- 待询
规格数量 - Fluo-4, pentasodium saltTD0049Calcium measurement is critical for numerous biological investigations. Fluorescent probes that show spectral responses upon binding calcium have enabled researchers to investigate changes in intracellular free calcium concentrations by using fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry, fluorescence spectroscopy and fluorescence microplate readers. Fluo-3 and Fluo-4 are most commonly used among the visible light-excitable calcium indicators. Fluo-4, pentasodium salt is an analog of fluo-3 with the two chlorine substituents replaced by fluorines, which results in increased fluorescence excitation at 488 nm and consequently higher fluorescence signal levels.
- ¥ 4200
规格数量 - Rhod-FF (potassium salt)T36389Rhod-FF is a difluorinated analog of the cell-impermeant calcium indicator rhod-2. It has a very low affinity for calcium (Kd = 320 μM). Low affinity calcium indicators are particularly useful for studying compartments with high concentrations of calcium, such as endoplasmic reticulum, where high affinity dyes will be insensitive to luminal fluctuations. Rhod-FF has excitation/emission maxima of approximately 552 and 580 nm, respectively.
- ¥ 1430
规格数量 - Indo-1 (sodium salt)T37091Indo-1 (sodium salt) is a ratiometric fluorescent calcium indicator. It is ideal for analyses using flow cytometry, as it uses a single excitation source, typically 349-364 nm light from an argon-ion laser. The emission maximum shifts from 475-485 nm without calcium to 400-410 nm when Indo-1 (sodium salt) binds calcium. Indo-1 (sodium salt) is prone to photobleaching, which limits its usefulness in methods involving microscopy.
- ¥ 3290
规格数量 - Rhod-5N AMT36388Rhod-5N AM is a cell-permeant acetoxymethyl ester of the fluorescent calcium indicator rhod-5N . As rhod-5N AM enters cells, it is hydrolyzed by intracellular esterases to produce rhod-5N. Rhod-5N displays a low affinity for calcium (Kd = 19 μM). Low affinity calcium indicators are particularly useful for studying compartments with high concentrations of calcium, such as endoplasmic reticulum, where high affinity dyes will be insensitive to luminal fluctuations. Rhod-5N has excitation/emission maxima of approximately 551 and 576 nm, respectively.
- ¥ 11800
规格数量


















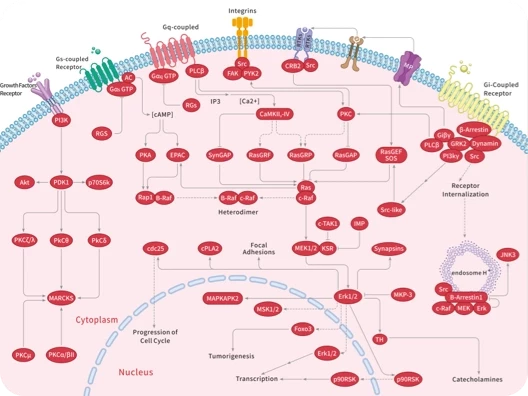
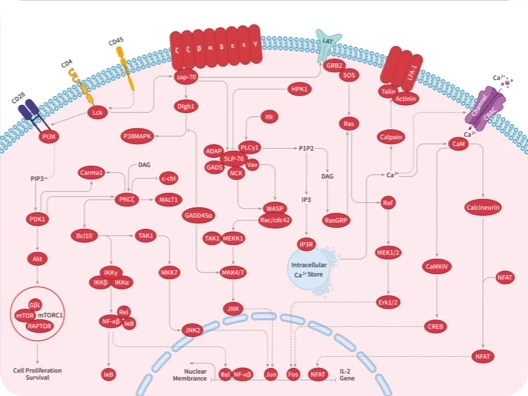
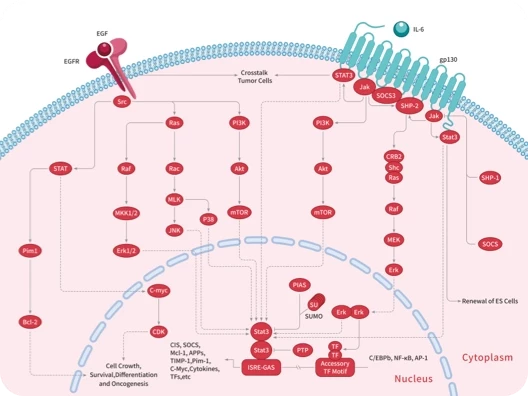
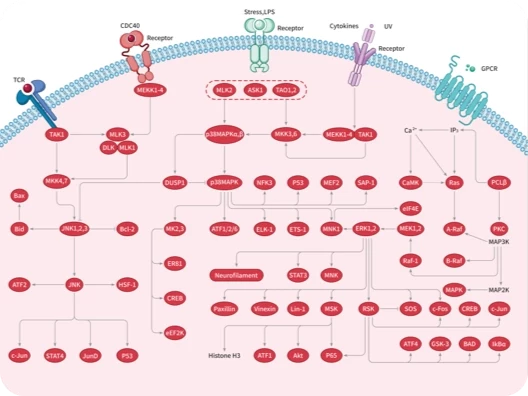

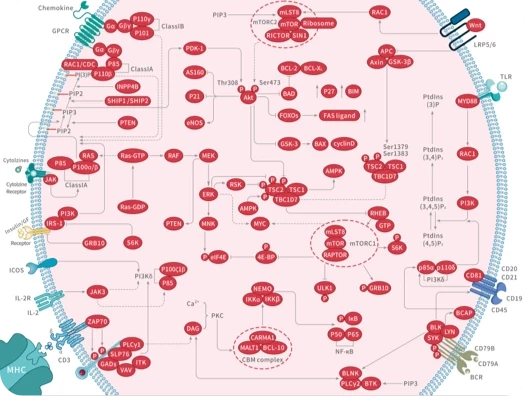
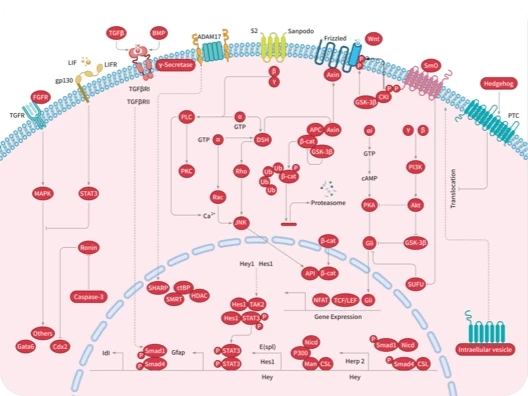
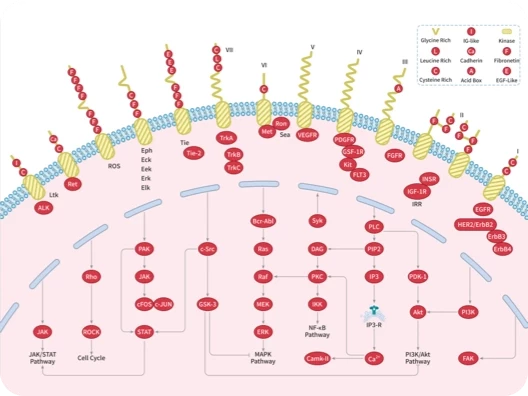
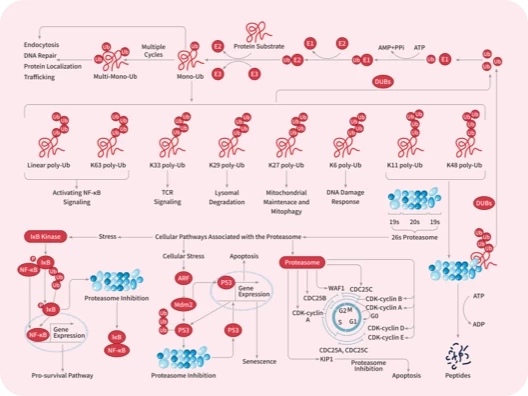

 |
|