- 全部删除
 您的购物车当前为空
您的购物车当前为空
Apolipoprotein L/APOL1 Protein, Human, Recombinant (His)
APOL1, also known as apolipoprotein L1, is a minor apoprotein component of HDL (High-density lipoprotein) or 'good cholesterol' which is synthesized in the liver and also in many other tissues, including pancreas, kidney, and brain. APOL1 belongs to the apolipoprotein L family. It may play a role in lipid exchange and transport throughout the body. It may also participate in reverse cholesterol transport from peripheral cells to the liver. Defects in APOL1 are the cause of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis type 4 (FSGS4). It is a renal pathology defined by the presence of segmental sclerosis in glomeruli and resulting in proteinuria, reduced glomerular filtration rate and edema. Renal insufficiency often progresses to end-stage renal disease, a highly morbid state requiring either dialysis therapy or kidney transplantation.

Apolipoprotein L/APOL1 Protein, Human, Recombinant (His)
| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 μg | ¥ 3,820 | In stock | |
| 100 μg | ¥ 6,530 | 5日内发货 | |
| 200 μg | ¥ 11,130 | 5日内发货 | |
| 500 μg | ¥ 22,510 | 5日内发货 |
产品信息
| 生物活性 | Activity testing is in progress. It is theoretically active, but we cannot guarantee it. If you require protein activity, we recommend choosing the eukaryotic expression version first. |
| 产品描述 | APOL1, also known as apolipoprotein L1, is a minor apoprotein component of HDL (High-density lipoprotein) or 'good cholesterol' which is synthesized in the liver and also in many other tissues, including pancreas, kidney, and brain. APOL1 belongs to the apolipoprotein L family. It may play a role in lipid exchange and transport throughout the body. It may also participate in reverse cholesterol transport from peripheral cells to the liver. Defects in APOL1 are the cause of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis type 4 (FSGS4). It is a renal pathology defined by the presence of segmental sclerosis in glomeruli and resulting in proteinuria, reduced glomerular filtration rate and edema. Renal insufficiency often progresses to end-stage renal disease, a highly morbid state requiring either dialysis therapy or kidney transplantation. |
| 种属 | Human |
| 表达系统 | Baculovirus Insect Cells |
| 标签 | C-His |
| 蛋白编号 | Q2KHQ6 |
| 别名 | FSGS4,apolipoprotein L1,APOL-I,APOL1,APO-L,APOL |
| 蛋白构建 | A DNA sequence encoding the human APOL1 (Q2KHQ6) (Met1-Leu398) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. Predicted N terminal: Glu 28 |
| 蛋白纯度 | ≥ 80 % as determined by SDS-PAGE. ≥ 90 % as determined by SEC-HPLC. 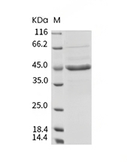 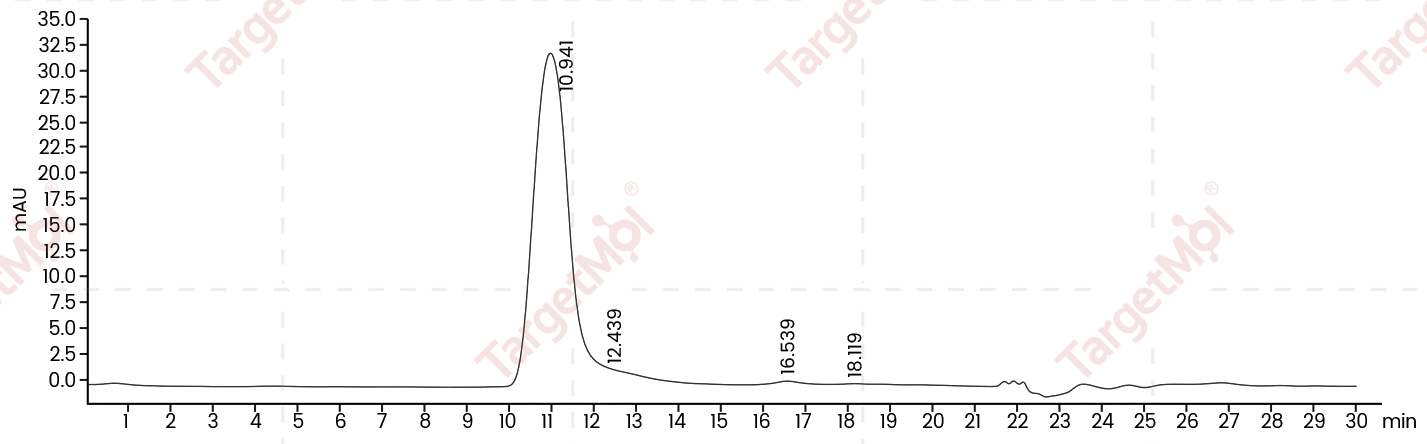 |
| 分子量 | 42.53 kDa (predicted); 44 kDa (reducing condition, due to glycosylation) |
| 内毒素 | < 1.0 EU/μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method. |
| 缓冲液 | Lyophilized from a solution filtered through a 0.22 μm filter, containing 20 mM Tris, 300 mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, 0.5 mM TCEP, pH 7.5. Typically, a mixture containing 5% to 8% trehalose, mannitol, and 0.01% Tween 80 is incorporated as a protective agent before lyophilization. |
| 复溶方法 | A Certificate of Analysis (CoA) containing reconstitution instructions is included with the products. Please refer to the CoA for detailed information. |
| 存储 | It is recommended to store recombinant proteins at -20°C to -80°C for future use. Lyophilized powders can be stably stored for over 12 months, while liquid products can be stored for 6-12 months at -80°C. For reconstituted protein solutions, the solution can be stored at -20°C to -80°C for at least 3 months. Please avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles and store products in aliquots. |
| 运输方式 | In general, Lyophilized powders are shipping with blue ice. |
| 研究背景 | APOL1, also known as apolipoprotein L1, is a minor apoprotein component of HDL (High-density lipoprotein) or 'good cholesterol' which is synthesized in the liver and also in many other tissues, including pancreas, kidney, and brain. APOL1 belongs to the apolipoprotein L family. It may play a role in lipid exchange and transport throughout the body. It may also participate in reverse cholesterol transport from peripheral cells to the liver. Defects in APOL1 are the cause of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis type 4 (FSGS4). It is a renal pathology defined by the presence of segmental sclerosis in glomeruli and resulting in proteinuria, reduced glomerular filtration rate and edema. Renal insufficiency often progresses to end-stage renal disease, a highly morbid state requiring either dialysis therapy or kidney transplantation. |